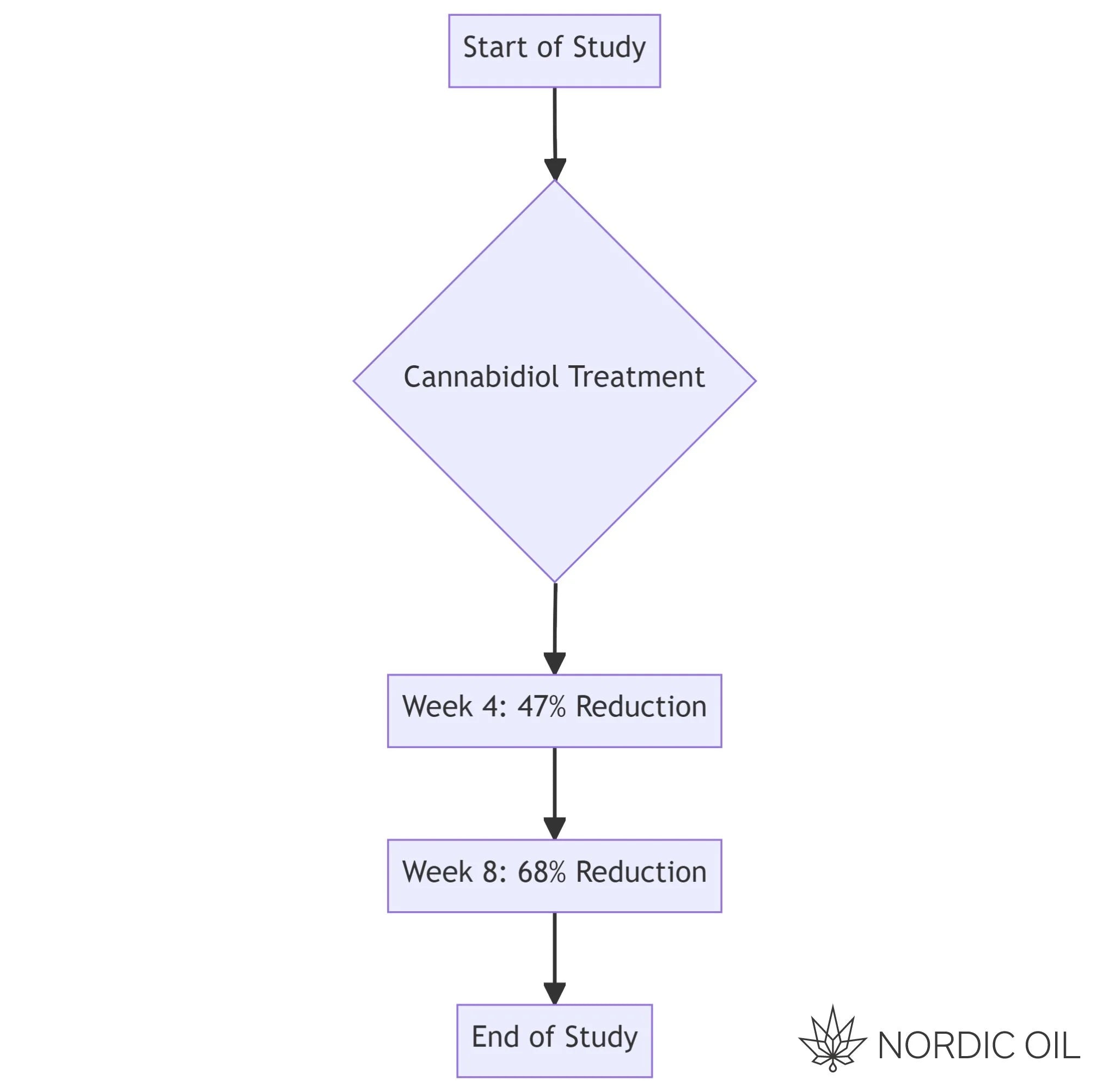
The study we're looking at is a review of literature, meaning it's a comprehensive look at previous research on the subject. It was conducted by a team of researchers from the Neurosciences Institute at the University Miguel Hernández-CSIC and the Network for Addiction Disorders in Spain.
Main Findings:
- CBD shows potential as a treatment for anxiety, depression, and psychotic disorders.
- Its effects depend on factors like dosage, strain of cannabis, and method of administration.
- CBD interacts with several key targets in the brain, including cannabinoid and serotonin receptors.
- Early clinical trials support the efficacy of CBD in treating these disorders.
Methodology:
This study is a review, meaning the researchers analyzed and summarized findings from a range of previous studies. They looked at both animal and human studies to understand how CBD affects the brain and behavior. They also considered factors like the dosage of CBD used, the strain of cannabis, and how it was administered. This comprehensive approach allowed them to draw conclusions about the potential therapeutic use of CBD.
Potential Implications:
If CBD is proven to be an effective treatment for these mental health disorders, it could be a game-changer. Current treatments for these conditions are not always effective and can have unwanted side effects. CBD, on the other hand, has a positive risk-benefit profile, meaning its potential benefits outweigh its potential risks.
Limitations:
While the findings are promising, more research is needed. The effects of CBD can vary depending on a range of factors, and it's important to understand these fully. Also, most of the current evidence comes from animal studies, so we need more human trials to confirm these findings.
Conclusion:
So, could CBD be a new alternative for treating anxiety, depression, and psychotic disorders? The research is promising, but we're not there yet. As the authors of this study point out, we need large-scale studies to further evaluate CBD as a potential new drug for these conditions. But for now, the future looks hopeful. You can read more about this study here.